Go to: Histology of the periosteum Periosteum can be thought of as consisting of two distinct layers, an outer fibrous layer and an inner layer that has significant osteoblastic potential. In 1739, Duhamel noted that silver wires embedded under the periosteum became covered by osseous matrix.
Knee Cartilage Repair and Post-Surgical Treatment
The periosteum is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, [1] except at the articular surfaces (i.e. the parts within a joint space) of long bones. [nb 1] Endosteum lines the inner surface of the medullary cavity of all long bones. [2] Structure The periosteum consists of an inner cambium layer and an outer fibrous layer

Source Image: link.springer.com
Download Image
May 1, 2023Bone is a vascular structure and has a nervous supply also. The outer covering of the bone is known as the periosteum; the periosteum covers the whole surface of the bone except at the ligament attachment, tendon attachment, and an area covered by articulating cartilage. The periosteum is absent in sesamoid bones.

Source Image: researchgate.net
Download Image
Influence of Periosteum Location on the Bone and Cartilage in Tissue-Engineered Phalanx – ScienceDirect Go to: The periosteum Histology The periosteum comprises an outer fibrous layer and an inner cambium layer, which differ in terms of the proportions of cells, fibres and matrix.
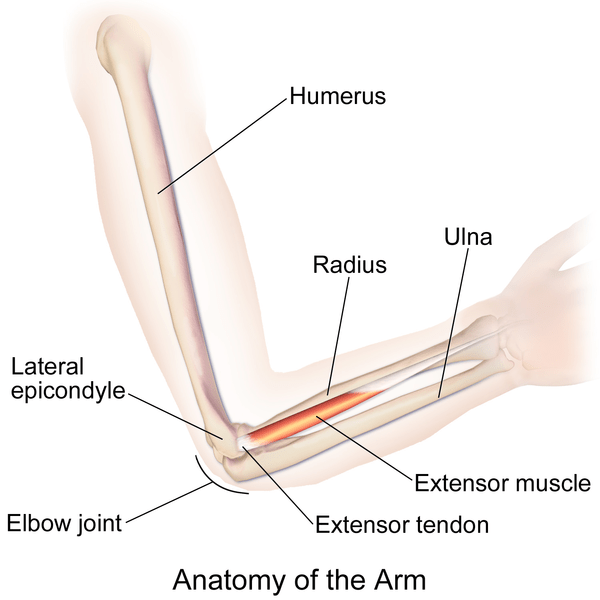
Source Image: biologyonline.com
Download Image
Why Doesn’T The Periosteum Cover The Articular Cartilage
Go to: The periosteum Histology The periosteum comprises an outer fibrous layer and an inner cambium layer, which differ in terms of the proportions of cells, fibres and matrix. the articular surfaces at the ends of bones are left without a periosteum, thereby allowing development of the articular cartilage [10]. As the joint cavitates, the fibrous capsule is formed along the periphery of the mesenchymal/ cartilag-inous model just as the periosteum/perichondrium formed more proximally along the same nascent bony model
Diarthrodial joint Definition and Examples – Biology Online Dictionary
Policy Function What does the periosteum do? The periosteum has three functions: Supplying blood to your bones. Giving them their sense of feeling. Growing and repairing your bones. Blood vessels in the periosteum connect back to your circulatory system to supply fresh, oxygen-rich blood to your bones. Long Bone Structure Diagram – Classful

Source Image: classful.com
Download Image
How does bone marrow produce blood, and how does the new blood get out of the bone itself and into the bloodstream? – Quora Policy Function What does the periosteum do? The periosteum has three functions: Supplying blood to your bones. Giving them their sense of feeling. Growing and repairing your bones. Blood vessels in the periosteum connect back to your circulatory system to supply fresh, oxygen-rich blood to your bones.
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Knee Cartilage Repair and Post-Surgical Treatment Go to: Histology of the periosteum Periosteum can be thought of as consisting of two distinct layers, an outer fibrous layer and an inner layer that has significant osteoblastic potential. In 1739, Duhamel noted that silver wires embedded under the periosteum became covered by osseous matrix.
Source Image: portobellophysio.ie
Download Image
Influence of Periosteum Location on the Bone and Cartilage in Tissue-Engineered Phalanx – ScienceDirect May 1, 2023Bone is a vascular structure and has a nervous supply also. The outer covering of the bone is known as the periosteum; the periosteum covers the whole surface of the bone except at the ligament attachment, tendon attachment, and an area covered by articulating cartilage. The periosteum is absent in sesamoid bones.

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Premium Vector | Superior sagittal sinus bone dura mater subdural space falx cerebri brain periosteum skin The periosteum covers the entire outer surface except where the epiphyses meet other bones to form joints (Figure \(\PageIndex2\)). In this region, the epiphyses are covered with articular cartilage, a thin layer of hyaline cartilage that reduces friction and acts as a shock absorber. Figure \(\PageIndex2\): Periosteum and Endosteum.

Source Image: freepik.com
Download Image
BL 17 Flashcards by Hannah Strafford | Brainscape Go to: The periosteum Histology The periosteum comprises an outer fibrous layer and an inner cambium layer, which differ in terms of the proportions of cells, fibres and matrix.

Source Image: brainscape.com
Download Image
Musculoskeletal Systems in the Animal Kingdom | Let’s Talk Science the articular surfaces at the ends of bones are left without a periosteum, thereby allowing development of the articular cartilage [10]. As the joint cavitates, the fibrous capsule is formed along the periphery of the mesenchymal/ cartilag-inous model just as the periosteum/perichondrium formed more proximally along the same nascent bony model
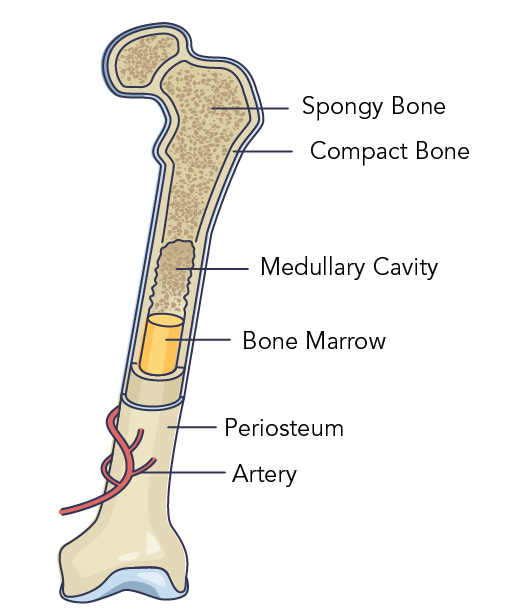
Source Image: letstalkscience.ca
Download Image
How does bone marrow produce blood, and how does the new blood get out of the bone itself and into the bloodstream? – Quora
Musculoskeletal Systems in the Animal Kingdom | Let’s Talk Science The periosteum is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, [1] except at the articular surfaces (i.e. the parts within a joint space) of long bones. [nb 1] Endosteum lines the inner surface of the medullary cavity of all long bones. [2] Structure The periosteum consists of an inner cambium layer and an outer fibrous layer
Influence of Periosteum Location on the Bone and Cartilage in Tissue-Engineered Phalanx – ScienceDirect BL 17 Flashcards by Hannah Strafford | Brainscape The periosteum covers the entire outer surface except where the epiphyses meet other bones to form joints (Figure \(\PageIndex2\)). In this region, the epiphyses are covered with articular cartilage, a thin layer of hyaline cartilage that reduces friction and acts as a shock absorber. Figure \(\PageIndex2\): Periosteum and Endosteum.