views 2,467,078 updated Ming Dynasty (1368-1644): Foreign Trade Sources Tribute System. Over time the Chinese government developed a mechanism known as the “tribute system” to deal with the outside world.
Step Inside: Lady Tan’s Circle of Women: Historical Ming Dynasty China | Official Website of Lisa See
The imperial Ming Dynasty ruled China from 1368 to 1644. It replaced the Mongol Yuan dynasty which had been in power since the 13th century. Despite challenges from abroad and within, the Ming dynasty oversaw an unprecedented growth in China’s population and general economic prosperity. The Ming were succeeded by the Qing dynasty (1644-1911).

Source Image: woodwardavenue.org
Download Image
Jan 4, 2024The Ming dynasty, which succeeded the Yuan (Mongol) dynasty (1206-1368), was founded by Zhu Yuanzhang. Zhu, who was of humble origins, later assumed the reign title of Hongwu. The Ming became one of the most stable but also one of the most autocratic of all Chinese dynasties. The basic governmental structure established by the Ming was
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Enumerating the greatest contributions of China to Art and Culture! | by Ujjaini Basu | Medium Currency The early Ming dynasty attempted to use paper currency, with outflows of bullion limited by its ban on private foreign commerce. [1] Like its forebears, the currency experienced massive counterfeiting and hyperinflation. (In 1425, Ming notes were trading at about 0.014% of its original value under the Hongwu Emperor.)
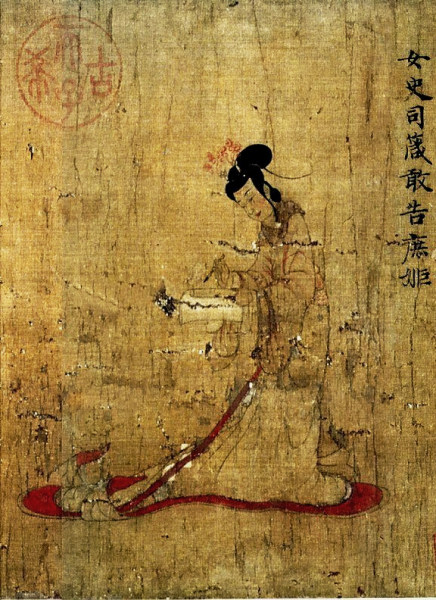
Source Image: chinasage.info
Download Image
Why Did The Ming Dynasty Restrict Trade With Europe
Currency The early Ming dynasty attempted to use paper currency, with outflows of bullion limited by its ban on private foreign commerce. [1] Like its forebears, the currency experienced massive counterfeiting and hyperinflation. (In 1425, Ming notes were trading at about 0.014% of its original value under the Hongwu Emperor.) Both European technology and European ideas were beginning to have some effect on China, albeit still very limited. China – Relations, Diplomacy, Trade: Whereas in Ming times the Chinese organized themselves along wholly bureaucratic and tightly centralized lines, the Ming emperors maintained China’s traditional feudal-seeming relationships
Chinese Painting: history, style and artists
copy page link CFOTO/Future Publishing via Getty Images The Ming Dynasty ruled China from A.D. 1368 to 1644, during which China’s population would double. Known for its trade expansion to the In the history of the Ming dynasty and western countries are not isolated | Paradox Interactive Forums
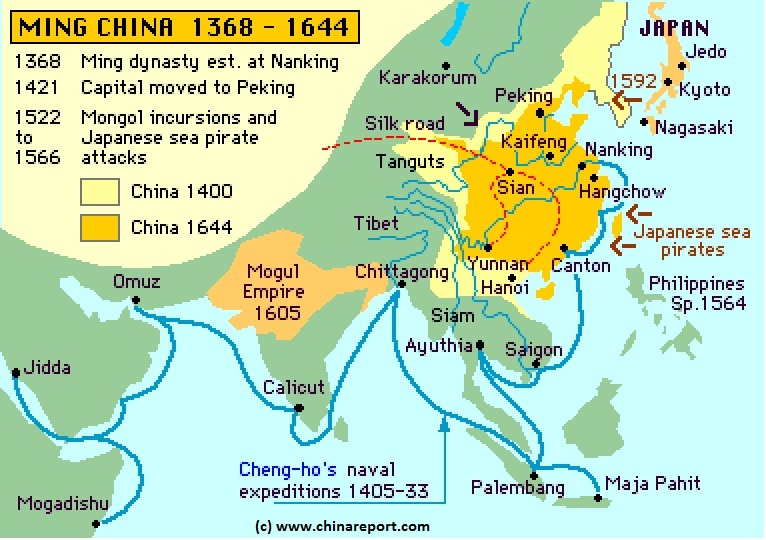
Source Image: forum.paradoxplaza.com
Download Image
EUROPEANS IN MING- AND EARLY-QING ERA CHINA (16th-18th CENTURIES) | Facts and Details copy page link CFOTO/Future Publishing via Getty Images The Ming Dynasty ruled China from A.D. 1368 to 1644, during which China’s population would double. Known for its trade expansion to the

Source Image: factsanddetails.com
Download Image
Step Inside: Lady Tan’s Circle of Women: Historical Ming Dynasty China | Official Website of Lisa See views 2,467,078 updated Ming Dynasty (1368-1644): Foreign Trade Sources Tribute System. Over time the Chinese government developed a mechanism known as the “tribute system” to deal with the outside world.

Source Image: lisasee.com
Download Image
Enumerating the greatest contributions of China to Art and Culture! | by Ujjaini Basu | Medium Jan 4, 2024The Ming dynasty, which succeeded the Yuan (Mongol) dynasty (1206-1368), was founded by Zhu Yuanzhang. Zhu, who was of humble origins, later assumed the reign title of Hongwu. The Ming became one of the most stable but also one of the most autocratic of all Chinese dynasties. The basic governmental structure established by the Ming was

Source Image: medium.com
Download Image
Teaching Early China and Ancient Rome Comparatively – Association for Asian Studies The Ming dynasty (/ m ɪ ŋ / MING), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty.The Ming dynasty was the last imperial dynasty of China ruled by the Han people, the majority ethnic group in China.Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established
Source Image: asianstudies.org
Download Image
The Role of Foreign Trade | World Civilization Currency The early Ming dynasty attempted to use paper currency, with outflows of bullion limited by its ban on private foreign commerce. [1] Like its forebears, the currency experienced massive counterfeiting and hyperinflation. (In 1425, Ming notes were trading at about 0.014% of its original value under the Hongwu Emperor.)

Source Image: courses.lumenlearning.com
Download Image
Ming dynasty | Dates, Achievements, Culture, & Facts | Britannica Both European technology and European ideas were beginning to have some effect on China, albeit still very limited. China – Relations, Diplomacy, Trade: Whereas in Ming times the Chinese organized themselves along wholly bureaucratic and tightly centralized lines, the Ming emperors maintained China’s traditional feudal-seeming relationships

Source Image: britannica.com
Download Image
EUROPEANS IN MING- AND EARLY-QING ERA CHINA (16th-18th CENTURIES) | Facts and Details
Ming dynasty | Dates, Achievements, Culture, & Facts | Britannica The imperial Ming Dynasty ruled China from 1368 to 1644. It replaced the Mongol Yuan dynasty which had been in power since the 13th century. Despite challenges from abroad and within, the Ming dynasty oversaw an unprecedented growth in China’s population and general economic prosperity. The Ming were succeeded by the Qing dynasty (1644-1911).
Enumerating the greatest contributions of China to Art and Culture! | by Ujjaini Basu | Medium The Role of Foreign Trade | World Civilization The Ming dynasty (/ m ɪ ŋ / MING), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty.The Ming dynasty was the last imperial dynasty of China ruled by the Han people, the majority ethnic group in China.Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established